With the advancement of computers, we can use them to aid us every day of our lives; some of us can’t go a day without them. These same computers introduced the concept of 3D or three Dimensional printing where we can model objects and create them using different techniques and design patterns with materials.
Today, we are going to uncover what exactly 3D Printing is and how it works under the hood with use cases, and types. We shall also see the difference between 2D and 3D styles in this same article. So let’s set the ball rolling.
What is 3D Printing?
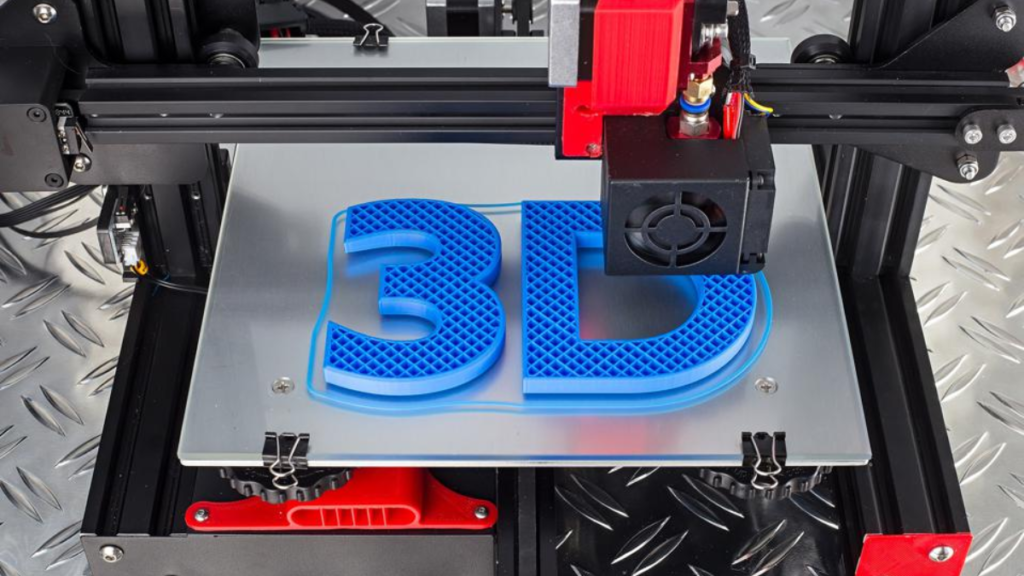
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is a method of creating a three-dimensional object layer-by-layer using a computer-created design. This means layers of material are built up to create a 3D part.
This type of printing is basically the construction of a three-dimensional object from a CAD model or a digital 3D model. It involves a manufacturing process that creates a physical object from a digital model file. The technology works by adding layer upon layer of material to build up a complete object.
Also Read The Best Affordable Printers You Can Get in 2022
How 3D Printing works
3D printable models may be created with a Computer-Aided Design (CAD) package, via a 3D scanner, or by a plain digital camera and photogrammetry software.

Three-dimensional printing is an additive manufacturing process that creates a physical object from a digital design. The process works by laying down thin layers of material in the form of liquid or powdered plastic, metal, or cement, and then fusing the layers together.
Types of 3D Printers
Today, proficient, minimal-expense work areas and benchtop 3D printers speed up advancement and usage in many industrial-related businesses. There are several types of 3D Printers but these three stand out; Stereolithography (SLA), Selective Laser Sintering (SLS), and Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM).
The printing time depends on a number of factors, including the size of the part and the settings used for printing. 3D printing can take anything from a few minutes to several hours or days.
Usecases
3D Printers have been utilized in assembling, clinical, modern, and sociocultural areas (for example Social Legacy) to make effective ad innovation (commercialization). As of late, 3D printing has largely been utilized in;
- Fashion Industry
- Automotives
- Clothing
- Fire Arms & Military
- Food Industry
- Transportation
- Health
2D Vs 3D Printing
3D printing is the method involved with making an article out of some material, frequently plastic. 2D printing, or just, printing, is the method involved with writing a picture down. They seem, by all accounts, to be two distinct cycles. Inside, be that as it may, the specialized functions behind the two kinds of printing have a few in number similitude.
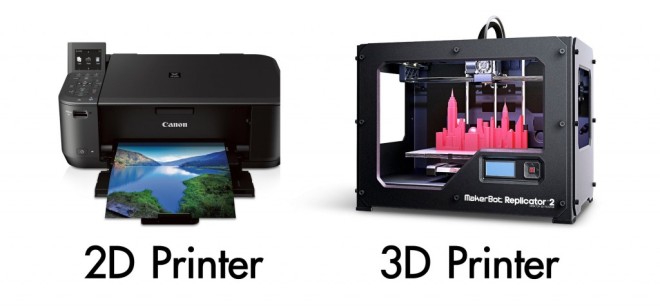
2D and 3D refer to the actual dimensions in a computer workspace. 2D is “flat”, using the horizontal and vertical (X and Y) dimensions, the image has only two dimensions and if turned to the side becomes a line. 3D adds the depth (Z) dimension.
Conclusion
As of now, 3D printing speeds are too delayed to ever be utilized in large-scale manufacturing. I believe they were part and parcel of the beginning of the third industrial revolution and their future use case is bright.
3D printing has progressed significantly since its initiation and it’s currently straightforward to get something 3D printed extremely quickly for a pretty modest.












