Streaming and downloading are the most common forms of accessing digital media on/from the internet. And while these terms are often (albeit erroneously) used interchangeably, they are two entirely different methods of obtaining contents electronically, and it is quite understandable if you easily get caught up in the to-stream-or-to download web. This is because both streaming and downloading possess their individual advantages and downsides. It is left for you to weigh in the factors and determine which one is best for you. In the paragraphs below, we’ll highlight the pros and cons of both processes and how to determine when it is best to stream media contents and when you should download instead.
Let’s talk about Streaming
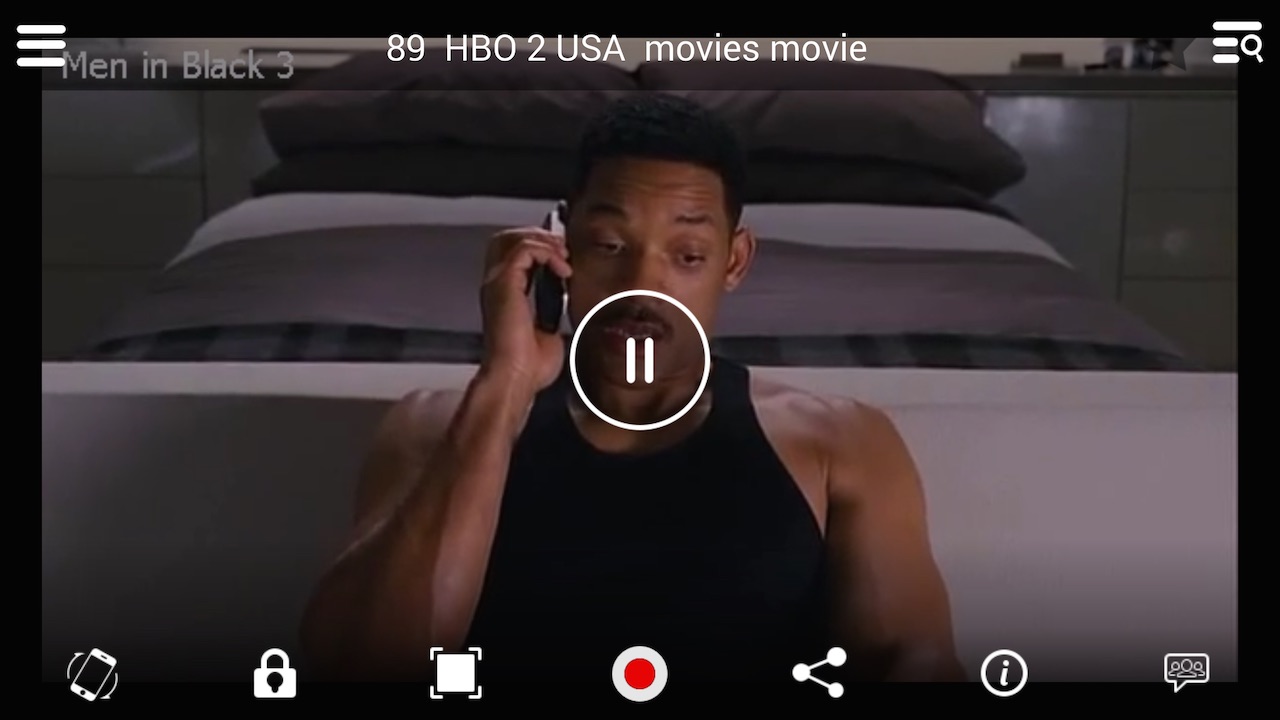
When you play content that isn’t saved on your device (phone, PC, tablet etc.) or from a source (like flash drives, external hard drives etc.) not physically connected to your device, that’s Streaming. Contents that are streamed are wirelessly accessed from a media server, a computer, or from your home/office network-attached storage which are all usually in a different location from the device you are streaming on. In simpler words, remotely playing shared media that is saved on another computer is termed Streaming.
Pros of Streaming
1. Convenience: Streaming hands you the capability of being able to watch almost anything (in whole or in part) you want without having to wait for the whole media file to download. You can start watching a video immediately while the rest of the file loads up — compared to downloading where the process could run into minutes or hours and you have to wait up until completion before you can play the media. Streaming allows you play contents even when the media is partly downloaded.
2. Flexibility: In a 2-hour long video, if only the concluding 20 minutes interest you, you can easily jump to that part of the video to watch it. This translates into the use of less bandwidth as data will be consumed only for the portion of the video you streamed; the skipped-over portions of content are never downloaded. Unlike downloading where you have to copy the media in its entirety to your device before you can watch any part of it, streaming offers more flexibility.
3. Access: Streaming hands you access to unlimited amount and type of contents, anywhere you are, on any device. As long as you have an internet connection and an internet-enabled smartphone or computer, you can stream audio and video contents and the best part: you don’t even have to have the file(s) saved on your device.
Cons of Streaming
1. Buffering: When streaming on a slow internet connection, the media file will stutter or pause, intermittently, causing a less enjoyable viewing experience. To avoid these interruptions and hiccups though, ensure you have a fast connection that conforms with the recommended internet speeds for streaming video online.
YouTube, Netflix and many other popular Video-on-Demand platforms have a minimum recommended internet speed for the various quality of videos they offer.
Advertisement - Continue reading below
2. High Battery Consumption: Because you are actively receiving audio and/or video signal as well as using cellular or WiFi network simultaneously, streaming is a power-intensive activity that sucks up your gadget’s battery juice faster.
3. Reduced quality: Streaming is adaptative. When streaming video, the quality supplied to your device is usually dependent on internet quality and speed; a number of video-on-demand websites will throttle audio and video quality based on these factors. Online music streaming isn’t left out too; the quality of streamed audio is not as high as saved MP3 files (according to MakeUseOf).
4. Source Dependability: The source, where the media file you are streaming from is located, must be on and connected. Else, the streaming stops. For example, if your home network-attached storage (NAS) device gets disconnected from its power source or the internet, you will not be able to remotely access (read: stream) media from it.
The source of the media must be connected and turned on, or the streaming stops.
And Downloading?
While streaming is the act of directly playing media (audio or videos) saved on someone else’s computer, downloading involves saving or storing or copying the file(s) from another computer to yours.
Pros of Downloading
1. Transferability: When you save a media file on your device, you can copy, move, or play it to other storage devices — unless it is copyright-protected. Downloaded media can also be streamed to other devices.
2. Availability: Downloading media files on your device means they are available to be watched and rewatched anytime; at your convenience, as many times as you want to.
3. Uses less bandwidth: Compared to streaming where a media file is re-downloaded each time you watch it –using more data in the process– re-watching a copy of downloaded media does not incur additional bandwidth.
Cons of Downloading
1. While downloaded media files don’t require you to constantly have an internet connection to watch them, you, however, must have sufficient storage space on your device to keep them available at all times.
2. Downloaded media files can easily get corrupted or (accidentally) deleted on your storage disk and devices.
When does it make sense to stream?
Streaming is the best option when you:
- Intend watching the video just one time
- Have huge or unlimited data or WiFi plan
- Have limited storage space on your device or storage drives
- Have a strong and reliable internet connection
When does it make sense to download?
- You should opt to download media files over streaming if:
- You intend playing the media multiple times in the future
- Have limited data plan
- Have more than enough space on your device
- Prefer your media in high, unadulterated quality
Understanding the differences between both processes of obtaining media (i.e streaming and downloading) is important. Knowing when to use them is even more important as it helps you save internet bandwidth, storage space, and also helps determine the best media player/streamer for your contents. It can also help you –as a site owner or administrator– decide if you want to embed a download link or direct media player on your web pages.
Discover more from Dignited
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.