Thunderbolt was earlier thought to be a replacement for USB but with Intel announcing that the forthcoming Thunderbolt 3 will have USB Type-C connectors, the path is much clear for a single port to feed all. In these times when having one of the two ports as a feature specification is becoming a consideration for purchase, device manufacturers are surely very confident about the future of connectivity.
What then is the difference between Thunderbolt 3 and USB-C? They surely can not be the same, and it is probably the reason for unison.
What are they?
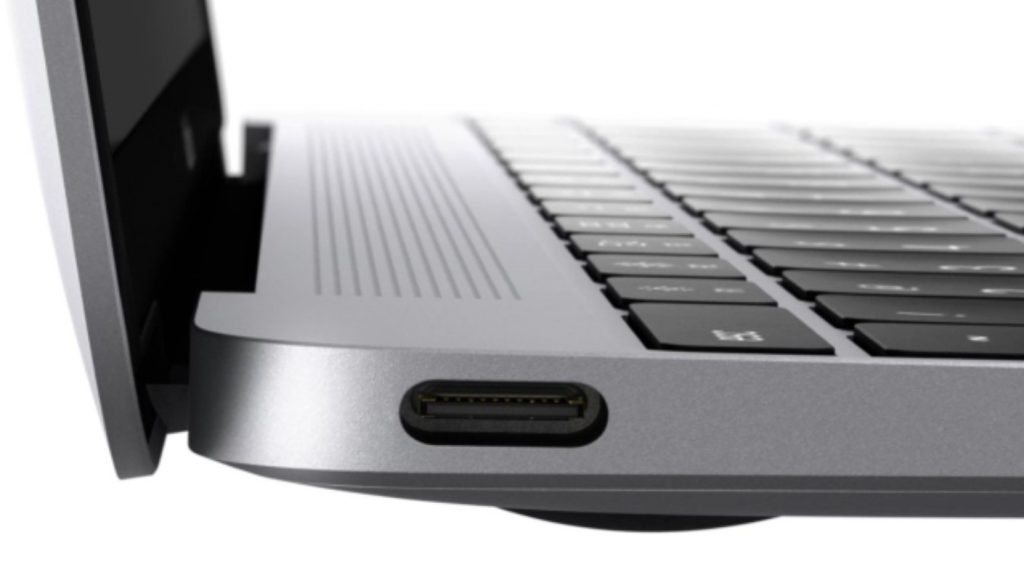
The USB-C is a standard, oval-shaped, connector that was developed by the USB Implementers Forum. It is compact and fully reversible, with both the up and down sides similar as well as both ends of its adapter designed to be the same. This implies that you do not have to mind the side of entry when inserting into a port, the way you would for USB-A or USB-B.
Thunderbolt 3, on the other hand, is an emerging technology for connecting external devices to PC that runs on a USB-C connector and cable. It is used to interconnect varying devices such as external hard drives, high-end audio interfaces and monitors, hubs, docks, expansion chases, as you wish; with just a limited amount of cable.
Read More: Everything you need to know about Thunderbolt 3
The difference
| Thunderbolt 3 | USB-C | |
|---|---|---|
| Data Transfer speeds | Up to 40Gbps | Up to 10Gpbs |
| Power Supply | 15 to 100 watts | 100 watts |
| Background Compatibility | Yes. Compatible with Thunderbolt and Thunderbolt 2 via a Thunder Adapter | Yes. Compatible with Older versions via adapter |
Power Supply
Thunderbolt 3 can provide 15 watts of power, with up to 100 watts of optional power, to their devices. USB-C can supply up to 100 watts of power to devices, reducing on the cable burden, and thus is the reason for its embedment in Thunderbolt 3.
Backward Compatibility
Thunderbolt 3 requires a Thunder Adapter to work with Thunderbolt and Thunderbolt 2 devices, just as USB-C’s USB 3.1 standard is compatible with USB 3.0 and USB 2.0 with an adapter.
Data Transfer Speeds
Thunderbolt 3 offers users a variety of connectors to meet their financial capabilities.
| Cable | Transfer Rates |
|---|---|
| Copper | Up to 20 Gbps |
| Copper | Up to 40 Gbps |
| Optical | Up to 40 Gbps over longer distances |
A typical port provides a maximum speed of 40 Gb/s throughout, four times faster than the ports that USB-C connectors use and any other external connector available. Thunderbolt devices transfer both audio and video data, steadily and simultaneously.
Support Features
USB-C cables can ably work with Thunderbolt 3 ports, just as Thunderbolt cables can work well with USB-C ports. The only limitation here is that the thunderbolt platform is only available on Intel processors implying that a cross-connection will not support thunderbolt features.
The notable difference between the two is that Thunderbolt 3 is a technology that uses USB-C for cabling and connections. You got that.
Discover more from Dignited
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.