One of the specs we often look at when we are checking out a phone is the RAM (random access memory). Together with other specs, we use it to gauge how well it will perform. Also referred to as phone memory, it is usually much smaller than the phone storage or ROM. It is much smaller than the internal storage because, unlike the ROM, it does not permanently store data. Instead, it serves as a temporary repository for storing data for running programs on your phone.
So you might be wondering, okay, why can’t the programs be run from the internal storage? Or what is the need for a temporary storage anyway? The first thing to know is that the processor is responsible for running these programs and it operates at a comparatively higher frequency or speed. In that regard, the internal storage can not possible keep up with it and the RAM is much faster and its specifically designed for that purpose.
Read More: Types of LPDDR RAM: Understanding Mobile Computer Memory
Back to what happens to your phone RAM when it is full, but before we go further you should understand how phone memory works first.
How Does Phone RAM Work
The way the RAM works on smartphones is a bit different from the way it works on computers. The RAM is generally partitioned into the core RAM and the ZRAM. In the core RAM, the program is loaded in like it normally does and the processor can then run it by accessing the program data via the memory controller. In the ZRAM, the data it carries is compressed and has to be decompressed before it can be accessed In other words, the ZRAM helps to save memory space since the data in it is cmpressed to a fraction of its actual size.
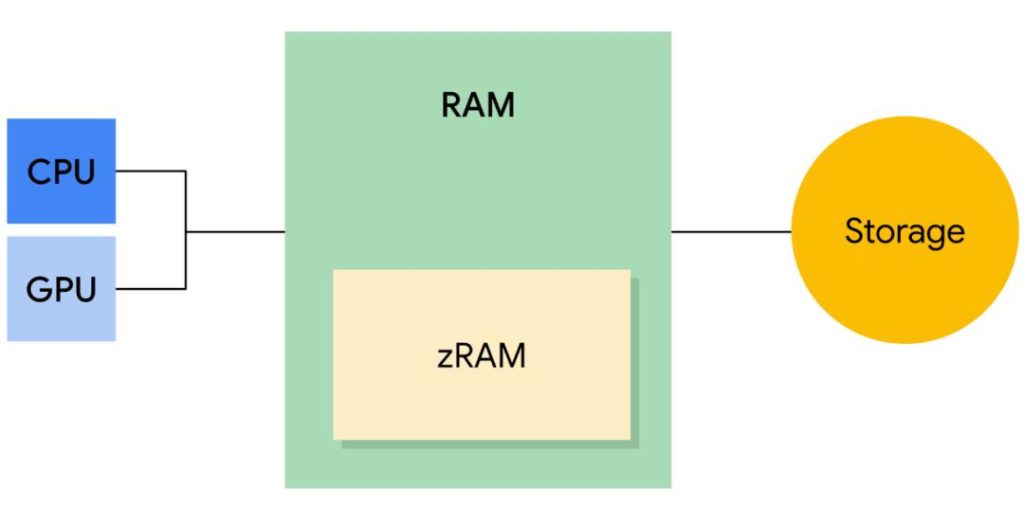
This way, your phone can shift low piority background processes to the ZRAM to save space on the core RAM. Also, you have the virtual memory or extended memory which is like a swap partition which is a fancy word for using a partitioned part of your internal storage as memory. and we will talk about later in this article.
In order of priority, the phone system decides which process on the RAM takes precedence, it decides which one be moved to the ZRAM. Consequently, if that is full, then the part of the storage partitioned as virtual memory is used It slows the phone down because the internal storage used as a secondary memory is much slower than the main memory.
Some smartphones don’t essentially have ‘virtual RAM’ but instead closes background apps to make space for the app running that needs memory space. Before it is closed, the app is allowed to save its activity onto the ROM so you can resume where you left off. However, if you use an iPhone, you definitely have virtual memory on your phone.
SEE: How much RAM is enough for your smartphone?
Vivo recently introduced extended RAM (up to 3GB) on their smartphone and Xiaomi will allow users to have up to 2GB of virtual storage with the release of MIUI 13. Other OEMs have also been buying into the idea of having virtual RAM on their device but there is a caveat in using your internal storage as virtual memory. Phone ROM uses flash storage which has a read/write life span, using it has RAM which involves a lot of read/write processes will invariably shorten the life span of your phone internal storage.