What is Thunderbolt? Simply put, Thunderbolt is a protocol that provides a set of features for a PC to interact with devices connected to it. Some of the most common uses for a Thunderbolt interface are connecting to monitors, connecting to storage devices, file transfer, and transmission of audiovisual signals.
Thunderbolt interfaces can also be used to charge devices as well. Additionally, Thunderbolt can daisy-chain devices together such as a display to your hard drive and a hard drive to your computer.
We are currently in the 4th generation of Thunderbolt technology. We saw the genesis of this technology from Intel in 2011 with speeds of 10 Gbps which has since grown 4 folds to 40Gbps. At the time, USB 3.0 was reigning at 5Gbps. Having used the Thunderbolt technology for over a decade, in 2022, Apple being the most prominent and consistent supporter of this Technology introduced the latest Silicon Macs with Thunderbolt 4 ports.
Also Read: Thunderbolt 3 vs USB Type-C: What are the key differences
What Is Thunderbolt 3?
Connection-wise, Thunderbolt 3 uses a USB-C interface mainly for simplicity but there are more reasons. The earliest generations of Thunderbolt used a Mini DisplayPort connector but hardly any laptops used such a port. However, with the introduction of USB-C to replace the Mini DisplayPort as the connector for Thunderbolt, it all made sense.
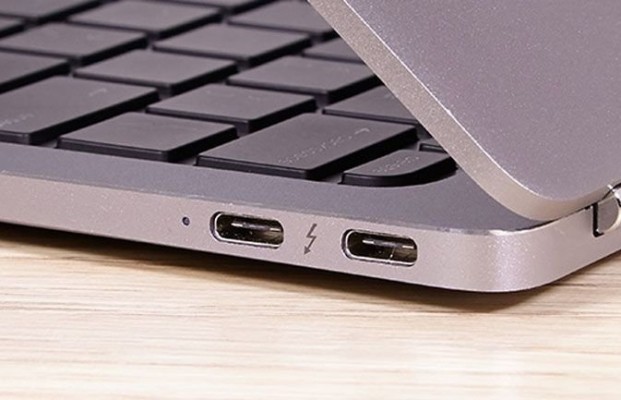

Thunderbolt 3 also supports the DisplayPort protocol which can be used to daisy chain and drive multiple 4K displays at 60hz using a single cable. This third generation saw a double in bandwidth speed from 20Gbps in Thunderbolt 2 to 40Gbps. Thunderbolt 3 also supports HDMI 2.0, DisplayPort 1.2, and 10GbE networking. Thunderbolt 3 is also backward compatible and can output audiovisual signals to two 4K displays or to one 5k monitor.
Also Read: Everything you need to know about Thunderbolt 3: Speed, Display, Power, and Connectivity
What Is Thunderbolt 4?
Released in July of 2020 as the successor to Thunderbolt 3, Thunderbolt 4 would ideally be a faster protocol, but it isn’t. Speed-wise, Thunderbolt 4 caps at 40Gbps just like Thunderbolt 3. Also, when it comes to the connector, Thunderbolt 4 retains the same USB-C port. So, what’s the upgrade?
The short answer is that this 4th generation focuses to improve security, reliability, compatibility, and stability. It can also be thought of as a more strict version, or supplement, to Thunderbolt 3. Keep reading below the long version answers.
Also Read: 5 uses of Thunderbolt 3 (USB-C)
Thunderbolt 3 vs Thunderbolt 4 Differences
1. Resolution
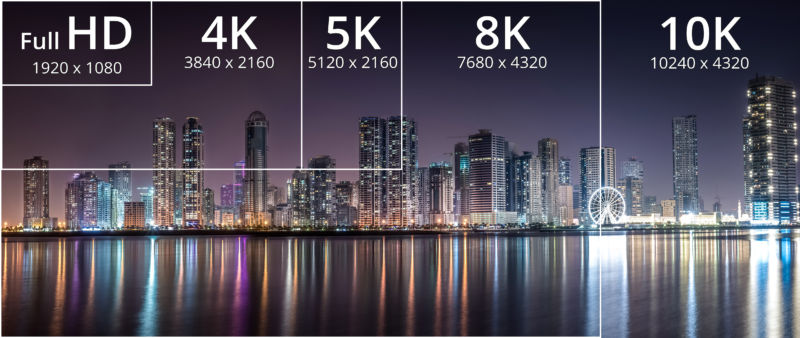
Increased video data support is the most important and notable upgrade. Recall when we highlighted that Thunderbolt 3 is capable of output to 2 displays at 4K or one display at 5K? Now, Thunderbolt 4 takes it up to 2 displays at 4K or one display at 8K!
Also Read: USB 4 vs Thunderbolt 3: What’s the difference
2. Wake From Sleep
This is one very nifty feature that lets users quickly start their computer using a peripheral such as a mouse or keyboard. The catch is that the peripheral device has to be connected to the computer via a Thunderbolt 4 port.
Also Read: What’s a Thunderbolt 3 Dock and what is it used for?
3. PCIe Speeds
The PCIe has gained improved data speeds from 16Gbps up to 32Gbps in Thunderbolt 4. This will be particularly useful for people who use external graphics cards.

Also Read: USB 3.0, 3.1, 3.2, 4.0 and Thunderbolt specs and feature comparison
4. Security
This 4th generation of Thunderbolt improves on the Direct Memory Access (DMA) protection by using Intel’s Virtualization Technology for I/O (VT-d). This restriction helps physically prevent attacks via DMA. For an ordinary user, this technology is unnecessary. However, for highly confidential data handlers, this is a big deal.
Also Read:
- Intel plans big on integrating Thunderbolt 3 in all its chips
- Thunderbolt 4 in the works with four times USB 3 Speeds, but there’s a catch
5. Charging
Another new requirement from Intel is that a Thunderbolt 4 certified device must be capable of 100W charging from at least one port.
Discover more from Dignited
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.