Throughout history, there have been sequences of events that are inevitable, beyond the control of any emperor or tyrant. In the past decade, words like Cryptocurrency, Blockchain, Stablecoins, Bitcoins, and digital currency began to frequently intersect.
But what exactly are these new technologies that tech enthusiasts are hopeful will define the future of payments and betting big on it? Follow along as we unpack the core principle behind these techs and what sets them apart.
What is Cryptocurrency?
Cryptocurrency is virtual money that takes the form of coins or tokens. In recent trends, some cryptos have ventured into the physical space with credit cards, but the large majority remain entirely digital.
The “crypto” in cryptocurrencies refers to cryptography. This allows for the creation and processing of digital money and their transactions kept decentralized across the whole chain/systems.
Alongside this important “crypto” attribute is a common commitment to decentralization; i.e making sure there is no issuer and always free of government or legal reserve interference.
The main built-in mechanism for issuance of the tokens is often, although not always, through a process called “Mining” and other controls.

Another important point to remember is all Cryptocurrencies modeled or released after Bitcoin are collectively called “altcoins” and typically present themselves as improved versions of Bitcoin.
Beyond that, the arena of cryptocurrencies is constantly evolving and expanding. The next great digital coin may be released tomorrow(you can’t be sure these days ) meanwhile Bitcoin is widely seen as a pioneer in the field of cryptocurrencies.
Also Read: How different is cryptocurrency from normal money?
Understanding Central Banks Digital Currencies
Central Banks Digital currency is one hot topic that will dominate the decade as there is a race to define a digital currency standard for the emerging digital economies especially In continents like Africa.
The foresees around two types of central bank digital currencies. The first is in the wholesale arena, mostly for payments between large commercial parties and financial institutions.
The second type of digital currency is in the retail realm. Retail digital currencies could be typically used in day-to-day transactions by households and businesses, and depending on their design, they could upend our existing financial system.
Users could pay with a CBDC just as today, with debit cards, smartphone-based apps, or online banking tools, all operated by a bank or other private sector payment provider.
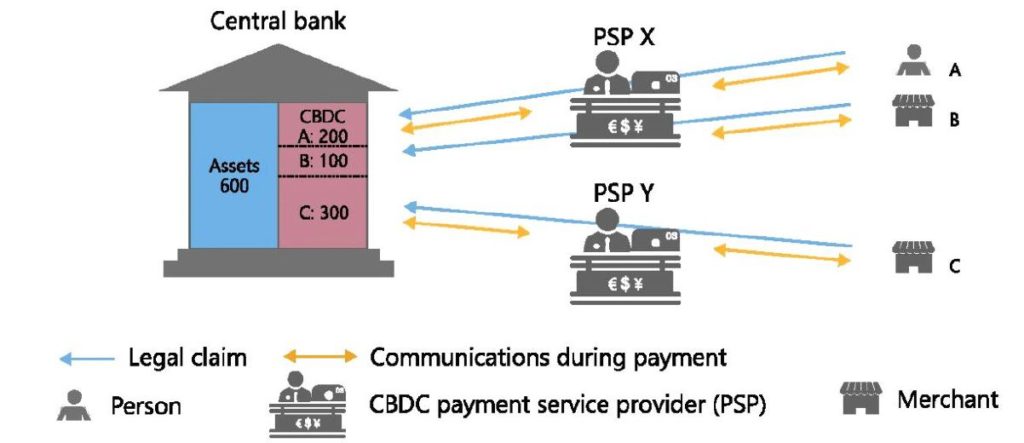
Keep in mind, digital currencies are new avenues and many central banks across the globe are researching and trying to find the best architecture design to make it become a complementary means of payment.
However, developing and Issuing a digital currency is a national choice and wherever issued, they will be an additional payment option that coexists with private sector electronic payment systems (visa, Mastercards, and any alternative) and cash.
What on Earth Are Stablecoins?
The main DNA of a Stablecoin lies in it’s umbilical cord connecting them to the existing financial systems or frameworks.
The privately issued digital currency is a type of cryptocurrency designed to be immune from market volatility and its values usually pegged against stable assets like gold or fiat currencies (the kind of currency issued by the government and regulated by the central bank).
They mainly fall into four broad categories;
- Fiat-collateralized stablecoins (Facebook Libra fall under this group)
- Crypto-collateralized stablecoins
- Commodity-collateralized stablecoins
- Non-collateralized stablecoins
Hundreds of stablecoins projects have been announced over the past years to varying degrees of success but one which stands out is Facebook’s Libra, which was recently renamed Diem.
Facebook’s ambitions of banking the unbanked across the globe have been dragged by a fragmented regulatory regime and non-existent frameworks for digital currencies.
It was forced to go back to the drawing table and set to relaunch again this year in 2021 as a tangible service for everyone. We can’t wait to see how it will evolve or be accepted.

Differences Between Stablecoins, Cryptos, and Digital Currencies
| Stablecoins | Digital Currency | Cryptocurrency |
| Partial regulation from the central banks and legal reserve | Purely regulated and Issued by central banks and legal reserves | Decentralised and no interference by central banks |
| Example include Facebook’s Libra (recently renamed to Diem) | Example includes Digital version of the Chinese Yuan and/or Sand Dollar | Popular examples are Bitcoin, Ethereum, Litecoin, DogeCoin |
| There is some element of identification | Account based identity issued and managed by the central bank | Complete anonymity and free from authority eyes |
| Mostly Corporate Owned | Government based currency | Open Blockchain networks |
| Partly market stable | Similar to traditional currency under most fronts | Market Volatile( fluctuations in value and price) |
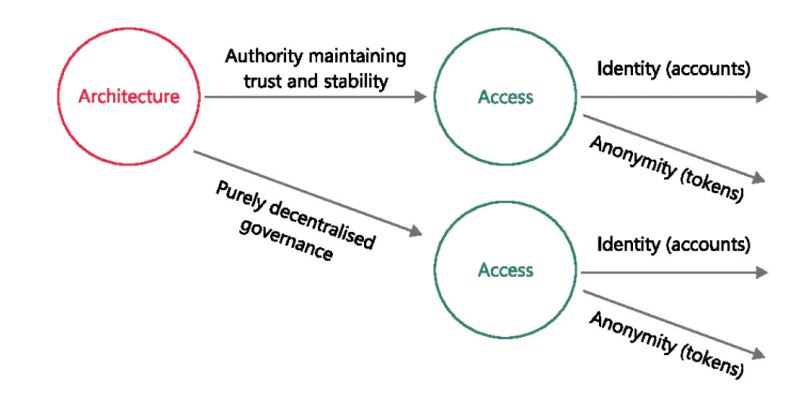
Should the payment system rely on a trusted central authority (such as the central bank) to ensure integrity and finality?
Or could it be based on a decentralized governance system, where the validity of payment depends on achieving consensus among network participants on what counts as valid payments? (the Bitcoin route).
Let us know in the comment section which route should the tech community embrace for what is set to be the “currency of the future”.